Blockchain
What Is a Layer 2?

Credit : cryptonews.net
Layer 2 blockchains are an essential a part of the Ethereum ecosystem. They’re constructed to onboard new customers and allow mass adoption of blockchain expertise. However how do Layer 2 blockchains make this attainable? And why are transactions cheaper and quicker on L2s? This information explains every little thing about Layer 2 scaling options.
What Is a Layer 2 in Blockchain?
The Definition of Layer 2
A Layer 2 community is a secondary blockchain that lives inside one other community referred to as Layer 1. It processes and executes transactions off the principle chain and sends the outcomes to the Layer 1 chain.
Layer 2 blockchains are often known as Layer 2 options as a result of they resolve scalability issues.
Why Blockchains Want Layer 2 Options
Layer 1 blockchains like Ethereum have scalability limitations. They want Layer 2 blockchains to deal with extra transactions per second (TPS) and to cut back fuel charges.
Additionally they speed up the adoption of cryptocurrencies and decentralized apps (dApps).
The Relationship Between Layer 1 and Layer 2
Layer 1 is the bottom chain that gives safety and consensus. Layer 2 handles 1000’s of transactions shortly and cheaply, but it surely nonetheless depends on a Layer 1 blockchain to confirm and finalize every little thing.
How Does a Layer 2 Work?
Off-Chain Processing and On-Chain Settlement
Layer 2 blockchains are appropriate with Ethereum. Customers can ship and obtain tokens or work together with sensible contracts on them. An L2 makes use of a unique mechanism to compute and course of transactions off-chain, making it extremely scalable.
Subsequent, L2s lump transactions collectively and ship them to the bottom layer. This step is determined by the kind of Layer 2 resolution getting used. Some options ship a cryptographic proof to the bottom layer. Others assume all transactions are legitimate.
Lastly, L2s ship the info to L1 via a sensible contract. The bottom layer resolves any disputes and provides legitimate transactions to the subsequent block.
Safety Inherited from the Base Layer
Layer 2 options inherit their safety from Ethereum. Such options have a sensible contract deployed on Layer 1. Different L2s depend on a bridge to speak. The sensible contract receives closing balances and the state of the L2 community. The bottom layer then verifies the submitted information via proofs or dispute mechanisms.
Since Layer 2 transactions occur off-chain, Ethereum turns into the last word supply of reality as a result of its consensus mechanism and immutability. Any fraud proofs, validity proofs, or state commitments submitted by L2 networks are in the end finalized on the bottom layer. This mitigates any malicious habits that takes place on L2 networks.
Transaction Velocity and Value Discount
Transacting on L2 networks is quick and low cost. Such secondary networks are glorious for frequent merchants. Transactions on Layer 2 networks are processed quick as a result of they undergo a sequencer. A sequencer is a server or a cluster of servers that processes transactions. It may be centralized or decentralized, and it might be operated by people, companies, or third-party operators.
Transacting on L2 networks is reasonable as a result of the sequencer bundles transactions and sends them to the bottom layer as a single transaction. This method splits the fuel charges of 1 base-layer transaction between L2 customers, which drastically reduces fuel charges.
Varieties of Layer 2 Options
Rollups (Optimistic Rollups, ZK-Rollups)
Rollups are a method to bundle tons of of transactions on Layer 2 networks right into a single transaction on Layer 1. There are two sorts of L2 rollups:
- Optimistic rollups
- Zero-knowledge proof (ZK) rollups.
Each sorts bundle Layer 2 transactions, however they work together with the bottom layer in another way.
Optimistic Rollups
Optimistic Rollups execute transactions off-chain and ship the info to the bottom layer through calldata or blobs. This method assumes that each one transactions are legitimate, therefore the title. Optimistic Rollups additionally compress transaction information earlier than sending it to Ethereum to cut back value.
When Ethereum’s sensible contract receives transaction information, anybody can problem this optimistic assumption utilizing fraud proofs inside a particular dispute window. Ethereum basically takes an “harmless till confirmed responsible” method when coping with Optimistic Rollups.
This dispute window varies and is determined by the Layer 2 resolution. And the individuals who problem this assumption are Ethereum contributors referred to as validators or watchers.
If a fraud proof succeeds, Ethereum reverts the invalid state, and the malicious sequencer is penalized by dropping its staked ETH collateral. The proper state is then enforced on the bottom layer.
If no legitimate fraud proof is submitted throughout the dispute interval, the batch of transactions is taken into account legitimate and finalized on Ethereum.
ZK-Rollups
Zero-knowledge-proof Rollups (ZK-rollups) work in an analogous method to Optimistic Rollups. They execute 1000’s of transactions off-chain and submit the info to sensible contracts that stay on the bottom layer. Nonetheless, as an alternative of assuming that each one transactions are legitimate, ZK-Rollups show that each transaction is legitimate earlier than sending it to Ethereum. That is achieved by producing cryptographic proofs, often known as zero-knowledge proofs, which mathematically confirm the correctness of all the batch.
ZK-rollups depend on an operator (aka prover or sequencer) to course of transactions, generate proofs, and ship them to Ethereum. Some rollups depend on centralized operators whereas others use semi-decentralized provers. Proofs are verified immediately, therefore there’s no dispute interval, and customers entry their funds instantly. As soon as the validity proof is accepted by Ethereum’s sensible contract, the transaction information is added to the subsequent confirmed block on the bottom layer.
State Channels
State channels are a unique method to scale Ethereum. A single state channel lets two or extra folks ship and obtain tokens, quick and low cost, with out on-chain settlement. As soon as they end transacting, they will submit the ultimate state and transaction abstract to Ethereum.
A state channel is peer-to-peer (p2p) and is ruled by a multi-signature sensible contract. To open a state channel, friends should lock funds in a sensible contract constructed on the bottom layer. The locked funds are collateral to make sure honesty and stop disputes. Any state change is executed and validated by these friends. This method reduces fuel charges, computation on Ethereum, and speeds transactions.
In case of a dispute between contributors, the difficulty is resolved on the bottom layer, the place the newest signed state might be enforced by Ethereum’s consensus.
State channels have some limitations. They require friends to remain on-line on a regular basis and monitor the channel. Additionally, they’re not user-friendly, and it’s tough to observe a number of channels concurrently.
Plasma Chains
A Plasma chain is a separate chain linked to the bottom layer, referred to as the foundation chain or dad or mum chain on this case. Plasma chains, additionally referred to as little one chains, are managed by a sensible contract deployed on the dad or mum chain.
Plasma chains course of and confirm transactions off-chain, decreasing verification masses on Ethereum. They depend on one operator or a number of operators to prepare and execute transactions, making them quicker. Nonetheless, solely the ultimate state is periodically submitted to Ethereum for safety anchoring.
To make the most of a Plasma chain, a person should deposit Ether or ERC-20 tokens into a sensible contract. The operator creates new tokens equal to the person’s funds. To exit the Plasma chain, a withdrawal request should be submitted. Then, the request is challenged through a fraud-proof for round 7 days. If the problem fails, the withdrawal request is authorized and executed. But when the problem succeeds, the operator is penalized.
Whereas Plasma chains appear to function like rollups, they’ve some limitations. Lengthy exit queues from a Plasma chain to Ethereum face a vital subject of information unavailability. It’s because the Plasma chain operator shops the info and solely submits it to Ethereum periodically. However, rollups present full transaction information each time a person desires to commerce or withdraw funds.
Sidechains (and why they differ from true L2s)
Sidechains will not be Layer 2 networks; nevertheless, they assist Ethereum scale. They’re separate blockchains that hook up with Ethereum via a bridge. Sidechains have totally different block specs and consensus mechanisms. They disinherit Ethereum’s safety properties and don’t publish transaction information or state roots again to Ethereum. This makes them liable to malicious assaults and centralization.
To realize excessive throughput, sidechains implement bigger block sizes and better fuel limits. Working larger blocks at quick processing instances requires highly effective {hardware}. This makes it tough for everybody to run a full node, leading to centralization and malicious assaults.
Sidechains are EVM-compatible, making Ethereum dApps run with minimal adjustments. Sidechains work together with Ethereum through a bridge, which is a set of sensible contracts deployed on each chains. The bridge implements a mint and burn mechanism, permitting customers to enter a sidechain, transact, and exit again to Ethereum.
Fashionable Layer 2 Initiatives in 2025
Arbitrum
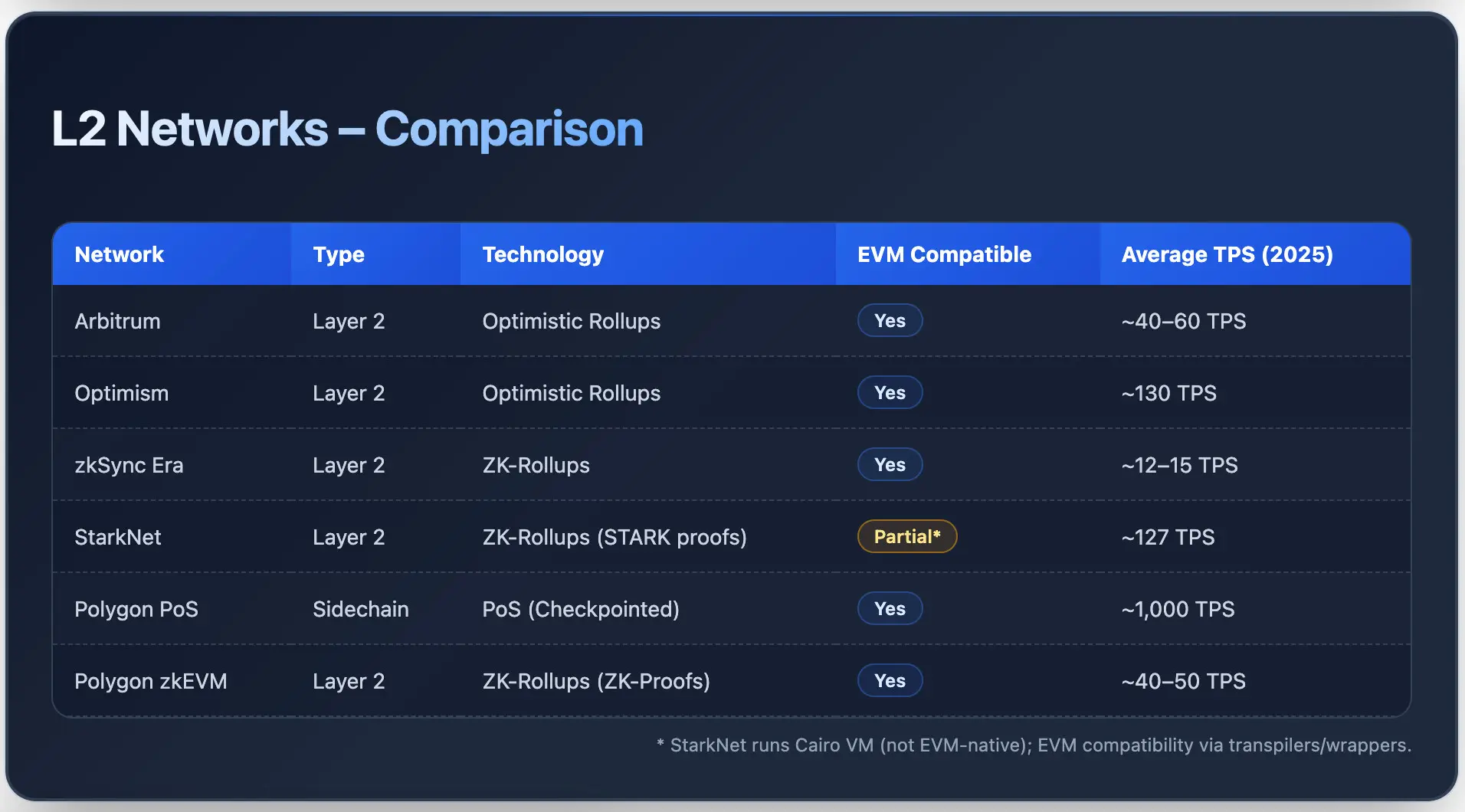
Arbitrum is an L2 that makes use of Optimistic Rollups to course of transactions off-chain and publish them to Ethereum. It presents decrease charges to merchants whereas counting on Ethereum’s safety.
Arbitrum helps the Ethereum Digital Machine (EVM), making it straightforward for builders to deploy sensible contracts with minimal adjustments. The L2 has a fleet of merchandise, together with Arbitrum One, Arbitrum Nova, and Arbitrum Orbit, which serve DeFi, gaming, and enterprise dApps.
The typical fuel value per transaction ranged between $0.007 and $0.015 in June of 2025. Swapping a token prices $0.30 on common, and transactions are finalized inside minutes.
Optimism
Optimism is an Ethereum-compatible L2 that depends on Optimistic Rollups. Similar to Arbitrum, Optimism executes transactions off-chain and sends the bundled information to Ethereum. The L2 presents low fuel charges and a excessive TPS charge.
Optimism is constructed with a modular OP Stack, which permits builders to deploy EVM sensible contracts with ease. As of 2025, the Optimism Superchain has processed 2.47 billion transactions and secured ~$3.4 billion in complete worth locked (TVL). The community has a mean block time of 200 milliseconds.
zkSync Period
zkSync Period is a layer 2 scaling resolution for Ethereum, and it makes use of ZK rollups. It really works in an analogous method to Optimism and Arbitrum; nevertheless, it’s totally different and makes use of ZK rollup expertise. zkSync processes transactions off-chain, proving their validity earlier than sending them to Ethereum.
The typical day by day transactions on zkSync grew from 290,000 in This fall 2024 to 1.1 million in Q1 2025. The typical charges additionally dropped to $0.03 per transaction in Q1 2025. Based mostly on information collected from zkSync’s blockchain explorer, the community has processed round 465 million transactions, with a mean block time of two to 4 seconds.
StarkNet
StarkNet is an L2 that makes use of ZK-rollups, or validity rollups, constructed on Ethereum. The L2 makes use of STARK proofs to make sure each off-chain transaction bundle is verified earlier than settlement on the bottom layer.
In mid-2025, StarkNet reached Stage 1 decentralization, a milestone in a framework for rollup networks proposed by Vitalik Buterin. It means StarkNet’s rollups have handed key technical and governance thresholds, bringing the community nearer to full decentralization.
StarkNet helps Cairo-based sensible contracts and native account abstraction. The typical transaction price on StarkNet is extraordinarily low, round $0.0013. The community recorded over 127 TPS in late 2024, with sub-2-second affirmation instances.
Polygon PoS and Polygon zkEVM
Polygon PoS is a high-throughput sidechain. It’s EVM-compatible and helps in scaling Ethereum. The sidechain makes use of a dual-layer structure and processes transactions off the bottom chain. It has periodic checkpoints making certain settlement and safety on Ethereum. Polygon PoS has a transaction throughput of ~1,000 TPS and helps tens of millions of customers with fuel charges beneath $0.01.
Polygon zkEVM is an L2 community. It’s totally EVM appropriate and makes use of ZK-Proofs to confirm transactions earlier than posting them on Ethereum. As of 2025, Polygon zkEVM processes round 40 to 50 TPS, with peak capability reaching over 200 TPS throughout testing. The typical fuel charges vary between $0.02 and $0.05 per transaction, which is about 90% cheaper in comparison with Ethereum.
Advantages of Layer 2 Blockchains
Decrease Transaction Charges
One of many foremost advantages of Layer 2 blockchains is decrease transaction charges. Throughout the 2021 bull market, Ethereum charged customers tons of and even 1000’s of {dollars} as a result of community congestion. Layer 2 networks resolve this by bundling transactions and splitting the price of a single Ethereum transaction amongst many customers, making charges minimal.
Quicker Transaction Speeds
Layer 2 networks provide near-instant transactions as a result of they depend on a sequencer to order and course of transactions shortly. Ethereum, however, takes longer to verify transactions as a result of its decentralized validator community.
Scalability for DeFi, NFTs, and Gaming
Layer 2 blockchains present the best playground for DeFi, NFTs, and gaming dApps to thrive and achieve mass adoption. Since transaction charges are negligible, sending and receiving cash or in-game gadgets and different sorts of NFTs is simple and nearly prompt.
Improved Person Expertise
L2 networks present a greater person expertise, particularly for brand new customers. They supply diminished latency, decrease entry prices, and simplify interactions with dApps. Customers profit from near-instant transactions and smoother entry to dApps with out experiencing congestion in comparison with the bottom layer.
Challenges and Dangers of Layer 2s
Safety Assumptions
Layer 2 networks inherit their safety from Ethereum however introduce their very own belief assumptions. Sequencers, bridges, and information availability layers can turn out to be vital factors of failure. If invalid information is submitted or if a proof problem fails, operators may lose their ETH stake, and customers may lose funds or expertise delays.
Person Expertise & Bridging Dangers
Shifting tokens between L1 and L2 or vice versa has some dangers. Customers may lose funds or expertise delays as a result of advanced UX or poor pockets integration, which drives customers away regardless of low charges and excessive throughput.
Centralization Considerations
L2 networks are technically centralized as a result of they depend on a sequencer operated by chosen validators. This might result in censorship, downtime, and technical failures, decreasing decentralization and person belief.
Regulatory Uncertainty
L2 networks function in a grey space. Establishments will not be adopting L2 networks in the meanwhile as a result of guidelines round custody, coin classification, and infrastructure are unclear.
Layer 2 vs Layer 1: Key Variations
Settlement and Safety
Layer 1 and Layer 2 networks function in another way by way of settlement and safety. L1s settle transactions straight, whereas L2s depend on the bottom chain settlement layer. L1s have full safety via a consensus mechanism and a community of validators, whereas L2s’ safety relies on Layer 1.
Velocity and Throughput
Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchains have totally different speeds and throughput charges. L1s, like Ethereum, are restricted to tens of transactions per second (round 10 to fifteen TPS).
L2 networks deal with tons of or 1000’s of TPS since they course of transactions off-chain.
In essence, L2s are quicker than L1s, making them best for real-time interactions with customers and dApps.
Use Circumstances and Commerce-Offs
L1s are glorious for high-value transactions the place decentralization is vital. For instance, Ethereum is utilized by stablecoin issuers and institutional DeFi platforms like Aave. L1s are additionally best for transferring NFTs like CryptoPunks and Pudgy Penguins since they’re high-value gadgets.
L2s are perfect for frequent, low-fee transactions like micropayments, gaming, or high-frequency buying and selling. L2 trade-offs are quick and low cost transactions, however with centralization and weaker safety.
The Way forward for Layer 2 Scaling
Ethereum’s Rollup-Centric Roadmap
Ethereum’s roadmap contains dank sharding and proto-dank sharding.
Beneath EIP-4844, proto-dank sharding will carry low cost blob information for L2s, whereas dank sharding goals to scale Ethereum rollups to 100,000 TPS. That is attainable by making L2 information considerable and cheaper.
The primary objective of the roadmap is to additional decrease L2 fuel charges whereas rising throughput. Furthermore, the improve will give attention to strengthening L1’s safety and settlement.
Cross-L2 Interoperability
Cross-L2 interoperability is an idea launched by Optimism. The idea named Superchain introduces seamless communication between OP Stack L2 chains.
Superchain goals to remove remoted rollups and merge safety and governance throughout a number of L2s. It will make it attainable to maneuver transactions between L2s via the Cross-L2 Inbox, bridging contracts, and standardized fault proofs.
Atomic cross-chain calls will likely be attainable, together with unification in fuel tokens and liquidity throughout L2s. For instance, OP Stack L2s equivalent to Base, Mode, Zora Community, and Frax Device can talk, forming a Superchain.
Layer 3 Options on the Horizon
Layer 3 options are totally different from L2s. Layer 2s are general-purpose scaling options for Ethereum, whereas L3s work on scaling dApps. L3s deal with personalized use instances to decrease charges and scale transactions, like in gaming, enterprise apps, or privacy-focused rollups.
StarkNet’s L3 Appchains, zkSync’s Hyperchains, and Arbitrum Orbit are examples of L3 implementations. These options let builders make the most of their very own rollups whereas inheriting L2 safety.
-

 Meme Coin7 months ago
Meme Coin7 months agoDOGE Sees Massive User Growth: Active Addresses Up 400%
-

 Blockchain1 year ago
Blockchain1 year agoOrbler Partners with Meta Lion to Accelerate Web3 Growth
-

 Videos1 year ago
Videos1 year agoShocking Truth About TRON! TRX Crypto Review & Price Predictions!
-

 NFT10 months ago
NFT10 months agoSEND Arcade launches NFT entry pass for Squad Game Season 2, inspired by Squid Game
-

 Meme Coin1 year ago
Meme Coin1 year agoCrypto Whale Buys the Dip: Accumulates PEPE and ETH
-

 Solana5 months ago
Solana5 months agoSolana Price to Target $200 Amid Bullish Momentum and Staking ETF News?
-

 Ethereum1 year ago
Ethereum1 year ago5 signs that the crypto bull run is coming this September
-

 Gaming1 year ago
Gaming1 year agoGameFi Trends in 2024


































